height of binary tree queries
You are given the root of a binary tree with n nodes. Each node is assigned a unique value from 1 to n. You are also given an array queries of size m.
You have to perform m independent queries on the tree where in the ith query you do the following:
- Remove the subtree rooted at the node with the value
queries[i]from the tree. It is guaranteed thatqueries[i]will not be equal to the value of the root.
Return an array answer of size m where answer[i] is the height of the tree after performing the ith query.
Note:
- The queries are independent, so the tree returns to its initial state after each query.
- The height of a tree is the number of edges in the longest simple path from the root to some node in the tree.
Example 1:
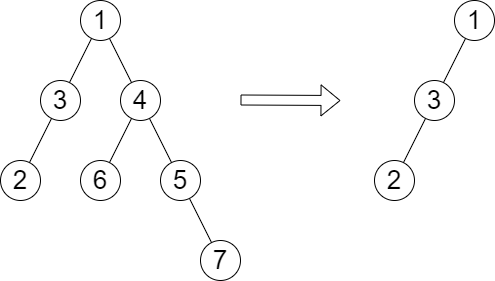
Input: root = [1,3,4,2,null,6,5,null,null,null,null,null,7], queries = [4] Output: [2] Explanation: The diagram above shows the tree after removing the subtree rooted at node with value 4. The height of the tree is 2 (The path 1 -> 3 -> 2).
Example 2:
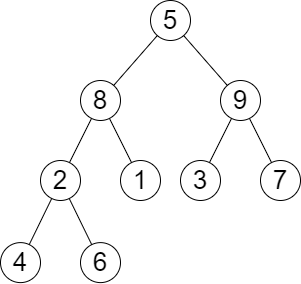
Input: root = [5,8,9,2,1,3,7,4,6], queries = [3,2,4,8] Output: [3,2,3,2] Explanation: We have the following queries: - Removing the subtree rooted at node with value 3. The height of the tree becomes 3 (The path 5 -> 8 -> 2 -> 4). - Removing the subtree rooted at node with value 2. The height of the tree becomes 2 (The path 5 -> 8 -> 1). - Removing the subtree rooted at node with value 4. The height of the tree becomes 3 (The path 5 -> 8 -> 2 -> 6). - Removing the subtree rooted at node with value 8. The height of the tree becomes 2 (The path 5 -> 9 -> 3).
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is
n. 2 <= n <= 1051 <= Node.val <= n- All the values in the tree are unique.
m == queries.length1 <= m <= min(n, 104)1 <= queries[i] <= nqueries[i] != root.valSolution
Overview
Approach 1: Left and Right Traversal
Intuition
Algorithm
- Initialize:
- a static array
maxHeightAfterRemovalto store the maximum height of the tree after removing each node. - a variable
currentMaxHeightto 0, which will track the current maximum height during traversals.
- a static array
- Initialize:
Call the
traverseLeftToRightmethod with the root node and initial height 0.Reset
currentMaxHeightto 0 for the second traversal.Now call the
traverseRightToLeftmethod with the root node and initial height 0.Initialize an array
queryResultsto store the results of the queries.Iterate through the queries:
- For each query, retrieve the corresponding maximum height from
maxHeightAfterRemoval. - Store this height in
queryResults.
- For each query, retrieve the corresponding maximum height from
Return the
queryResultsarray.Define a method
traverseLeftToRight:- If the current node is
null, return. - Store the current
currentMaxHeightinmaxHeightAfterRemovalfor the current node's value. - Update
currentMaxHeightto be the maximum of itself and the current height. - Recursively call
traverseLeftToRightfor the left and right child, incrementing the height.
- If the current node is
Define a method
traverseRightToLeft:- If the current node is
null, return. - Update
maxHeightAfterRemovalfor the current node's value to be the maximum of its current value andcurrentMaxHeight. - Update
currentMaxHeightto be the maximum of the current height and itself. - Recursively call
traverseRightToLeftfor the right and left child, incrementing the height.Approach 2: Single Traversal
Intuition
- The current
maxValon the path from the root to the node. - The node’s depth plus one (to include itself) and the height of its sibling subtree.
Algorithm
- The current
Initialize a map:
resultMapto store the maximum height of the tree after removing each node.heightCacheto store pre-computed heights of subtrees.
Call the
dfsmethod with initial parameters: root node,depth0,maxVal0,resultMap, andheightCache.Initialize an array
resultto store the final query results.Iterate through the queries:
- For each query, retrieve the corresponding maximum height from
resultMap. - Store this height in the
resultarray.
- For each query, retrieve the corresponding maximum height from
Return the
resultarray.Define the
heightmethod to calculate the height of a tree:- If the node is
null, return -1. - If the height of the node is already in
heightCache, return the cached value. - Calculate the height recursively as 1 plus the maximum of left and right subtree heights.
- Store the calculated height in
heightCache. - Return the calculated height.
- If the node is
Define the
dfsmethod for the depth-first search:- If the current node is
null, return. - Store the current
maxValinresultMapfor the current node's value. - Recursively call
dfsfor the left child:- Increment the depth.
- Update maxVal as the maximum of current maxVal and (depth + 1 + height of right subtree).
- Recursively call
dfsfor the right child: - Increment the depth.
- Update maxVal as the maximum of current maxVal and (depth + 1 + height of left subtree).
Approach 3: Subtree Size
Intuition
- Assign an index to each node
- Track the depth of each node
- The maximum depth from the left up to the starting index
- The maximum depth from the right beyond the ending index, if available.
Algorithm
Initialize a map:
nodeIndexMapto store the index of each node value.subtreeSizeto store the number of nodes in the subtree for each node.
Initialize lists
nodeDepths,maxDepthFromLeft, andmaxDepthFromRightto store node depths and maximum depths from left and right.Call the
dfsmethod to populatenodeIndexMapandnodeDepths.Store the total number of nodes in
totalNodes.Call
calculateSubtreeSizemethod to populate thesubtreeSizemap.Initialize
maxDepthFromLeftandmaxDepthFromRightwith the first and last node depths respectively.Iterate through the nodes to calculate
maxDepthFromLeftandmaxDepthFromRight:- Update
maxDepthFromLeftwith the maximum of the previous max and current depth. - Update
maxDepthFromRightwith the maximum of the previous max and current depth (in reverse order).
- Update
Reverse the
maxDepthFromRightlist.Initialize an array
resultsto store the query results.Process each query. For each query node:
- Calculate the end index as the node's index minus 1.
- Calculate the start index as the end index plus the subtree size plus 1.
- Initialize
maxDepthwith the value frommaxDepthFromLeftat the end index. - If the start index is within bounds, update
maxDepthwith the maximum of currentmaxDepthand the value frommaxDepthFromRightat the start index. - Store the
maxDepthin theresultsarray.
Return the
resultsarray.Define a method
dfsfor the depth-first search:- If the current node is null, return.
- Add the current node's value and index to
nodeIndexMap. - Add the current depth to
nodeDepths. - Recursively call
dfsfor left and right children, incrementing the depth.
Define a method
calculateSubtreeSize:- If the current node is
null, return 0. - Recursively calculate the size of left and right subtrees.
- Calculate the total size as left size plus right size plus 1.
- Store the total size in
subtreeSizefor the current node. - Return the total size.
Approach 4: Eulerian Tour
Intuition
Algorithm
Initialize a list
eulerTourto store the Euler tour of the tree.Initialize maps
nodeHeights,firstOccurrence, andlastOccurrenceto store information about each node.Call the
dfsfunction to build the Euler tour and populate the maps.Set
tourSizeto the size ofeulerTour.Initialize arrays
maxDepthLeftandmaxDepthRightof sizetourSize.Set the first element of
maxDepthLeftand last element ofmaxDepthRightto the height of the root node.Iterate from 1 to
tourSize - 1:- Set
maxDepthLeft[i]to the maximum of the previous max height and the current node's height.
- Set
Iterate backward from
tourSize - 2to 0:- Set
maxDepthRight[i]to the maximum of the next max height and the current node's height.
- Set
Initialize an array
resultswith the same length asqueries.For each query in
queries:- Set
queryNodeto the current query value. - Calculate
leftMaxandrightMaxas the max height to the left and right of the node's first occurrence, respectively. - Store the maximum of
leftMaxandrightMaxinresults.
- Set
Return the
resultsarray.Define the
dfsfunction:- If the current node is
null, return. - Add the current node's height to
nodeHeights. - Set the first occurrence of the current node in
firstOccurrence. - Add the current node's value to
eulerTour. - Recursively call
dfsfor left and right children, incrementing the height. - Set the last occurrence of the current node in
lastOccurrence. - Add the current node's value to
eulerTouragain. Approach 5: Two Largest Cousins
Intuition
- The maximum height at that depth, excluding the current node.
- The second-highest height at that depth, if the maximum height subtree is removed.
Algorithm
Initialize a map:
nodeDepthsto store the depth of each node.subtreeHeightsto store the height of the subtree rooted at each node.
Initialize maps
firstLargestHeightandsecondLargestHeightto store the first and second largest heights at each level.Call the
dfsfunction to populate these maps.Initialize an array
resultswith the same length asqueries.For each query in
queries:- Set
queryNodeto the current query value. - Set
nodeLevelto the depth of the query node. - If the height of the query node's subtree equals the first largest height at its level:
- Set the result to the sum of node level and second largest height at that level, minus 1.
- Set
Otherwise:
- Set the result to the sum of node level and first largest height at that level, minus 1.
Return the
resultsarray.Define the
dfsfunction:- If the current node is
null, return 0. - Add the current node's depth to
nodeDepths. - Recursively call
dfsfor left and right children, incrementing the level. - Calculate
currentHeightas 1 plus the maximum of left and right subtree heights. - Add the current node's subtree height to
subtreeHeights. - Set
currentFirstLargestto the first largest height at the current level. - If
currentHeightis greater thancurrentFirstLargest:- Update
secondLargestHeightat the current level withcurrentFirstLargest. - Update
firstLargestHeightat the current level withcurrentHeight.
- Update
- Else if
currentHeightis greater than the second largest height at the current level:- Update
secondLargestHeightat the current level withcurrentHeight.
- Update
- Return
currentHeight.
- If the current node is



Comments
Post a Comment